Introduction to Checks and Balances
The system of checks and balances is one that the United States has been founded as a method of decreasing corruption. This standard has been employed in other countries as well, with varying degrees of success as to that implementation. The AP® US Government exam will likely consider your understanding of what checks and balances are and how they relate to the entire system of government within the United States. This system is important to life as we know it and is extremely important to allowing the people to continue running the country in the way that we are used to.
This AP® US Government review will take a look at what checks and balances are, who they apply to and just why they are so important to the overall government system. It will also take a look at what can happen if checks and balances are not maintained and the ways that different parts of the government can choose to circumvent the checks and balances. It will also look at why this process of circumventing is actually extremely important for the continuation of the government and the implementation of the will of the people as well.
What Are Checks and Balances
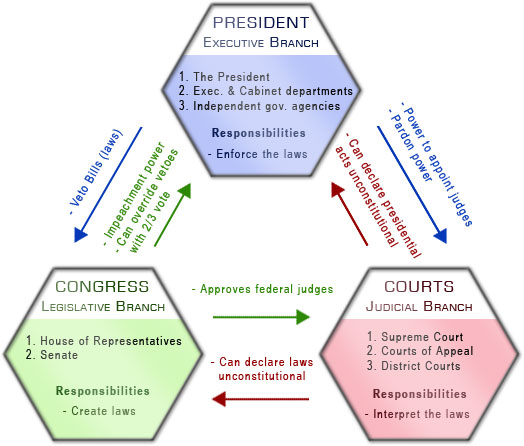
Checks and balances were written into the instruction manual for our government, and they are a way for each branch of government to balance out the power of the other. Our forefathers believed that it was important that no one person (or group of people) were more powerful than any other. As a result, they created a government that includes three different ‘branches.’ Those branches each have different responsibilities, but at the same time, they are required to work together in order to make decisions.
If the branches agree to a certain action, law or even inaction, the motion will pass, and the process goes smoothly. If they do not agree, however, that means the motion is not allowed. Without this system, one branch of the government would be able to make its own rules without regard for what the others want and even without regard for what the people want. This is the point of the system. When the government checks and balances the power of other branches, they are intended to keep them from acting in their best interests and instead lead them to act in the public’s best interests.
Checks mean that each branch is able to say no to the other. Balance means that each of them has the same amount of power as each of the others. By maintaining this system where all three branches are required and their power is equal, it is possible to maintain a type of status quo. The people are represented by all powers of the government, and no one can get too much power and therefore overthrow the government or the will of the people. This was what our forefathers were most afraid of after all.
Checks and Balances in the Executive Branch
The executive branch is responsible for the ‘execution’ of laws. That means that once the laws are created, they are the ones who make sure that the rest of the country is following those laws and continues to do so. The President is at the head of the executive branch and is the one who is responsible primarily for this though there are others, such as the Vice President and members of the Cabinet who assist him in this process.
The President, however, is not allowed to enact laws himself but he is allowed to call special sessions of Congress and veto bills, thus checking the power of Congress. He is also not allowed to make rulings on the violation of laws, but he is able to appoint the judges and give reprieves or pardons if he chooses, thus checking the judicial branch. At the same time, however, the other branches are not allowed to handle the execution of laws, which is the President’s responsibility alone. This provides the balance between the executive branch and other branches.
Checks and Balances in the Legislative Branch
The legislative branch is responsible for making laws. New laws can be proposed to Congress and they are responsible for voting on any of those laws. Even more, they can create their own laws by presenting it to the rest of Congress, discussing it and voting. Because this is an extremely important responsibility, Congress actually has a level of checks and balances within itself, in the form of two separate houses.
The Senate and the House of Representatives make up Congress and each discusses, presents and votes on new laws entirely separately. That means if a law is proposed in the House of Representatives and passed it must then go to the Senate to be discussed and passed and vice versa. Once this has happened, the law is then able to go to the President to be signed and passed or to be rejected if he believes the law is not in the best interests of the public.
The legislative branch checks the power of the President by maintaining the right to review all appointments and bring impeachment hearings and checks the power of the judicial branch also by the power to impeach and the ability to improve appointments.
Checks and Balances in the Judicial Branch
The judicial system is represented by the Supreme Court and federal courts established by Congress. The responsibility of the judicial branch is to review the laws passed by Congress and apply them to cases within the country. It is their responsibility to interpret the laws and the Constitution to determine if any laws passed are a violation. If a law is passed in violation of the Constitution, they are allowed to nullify it. If someone is accused of violating a law passed by Congress, they are responsible for determining if the law has truly been broken and what should be done about it.
The judicial branch’s power to nullify laws passed in violation of the Constitution allows them to ‘check’ the power of the legislative branch, ensuring they are not able to pass just any law they want. The judicial branch also ensures that any Presidential actions are not a violation of his powers or the Constitution and can nullify those actions that are found to be a violation. In this way, the judicial branch can check the powers of the other two branches. This helps to provide the balance necessary to keep each of the branches at the same level with no one more powerful, even the President.
Avoiding Checks and Balances
In order to maintain the level of checks and balances, it is important that each branch is able to stop the power of the others. This forms a system that is able to interact with each other but also stay with a balance of power. If the system did not allow for each branch of government to control the power of the other, it could result in problems for the way the country is run. It is important to understand how this works, however, and what each branch can do to the others.
Congress has the power to make laws. Once they make the law, it must go to the President who must approve it before it’s established in the country. Then the law must be reviewed by the judicial branch (when it is called for) to ensure it is Constitutional. But if the President does not want to approve the law he can choose to veto it. This is a way that the President can check the power of Congress. If the judicial branch reviews the law and finds it is unconstitutional, they also can veto it.
Now the additional checks come in because if the President veto’s a law that Congress has passed they still have the ability to pass it as long as they can get a 2/3 majority in both houses of Congress. They can then override the President’s veto. This is how the government ensures that the President is doing what the people want. If Congress can overwhelmingly agree that the law is in the best interests of the people, even the President is not able to stop it from becoming a law.
Checks and Balances & the AP® US Government Exam

The AP® US Government exam is likely to ask you to look at the way checks and balances impact each branch of the government and how this helps the country as a whole. For example, past exams have required an explanation of how each branch of government checks the executive branch. It may also require you to consider why these checks are important and why our forefathers decided that they should be included in the establishment of our government. Understanding the three different branches and how they link with each of the other branches is important, as this shows what each branch does in relation to the other branches. This is almost certain to be an important aspect of this subject in the AP® US Government exam.
Looking for AP® US Government practice?
Check out our other articles on AP® US Government.
You can also find thousands of practice questions on Albert.io. Albert.io lets you customize your learning experience to target practice where you need the most help. We’ll give you challenging practice questions to help you achieve mastery of AP® US Government.
Start practicing here.
Are you a teacher or administrator interested in boosting AP® US Government student outcomes?
Learn more about our school licenses here.








