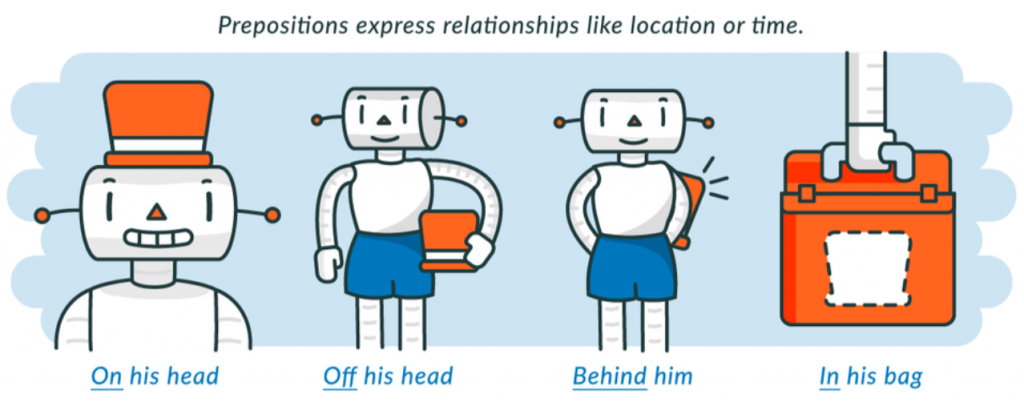
What is a preposition? A preposition expresses relationships between nouns. It can be used to indicate location, time, direction, and position. Usually, the preposition is part of a prepositional phrase.
For example:
- The vibrant, orange top hat rested on his head.
- In this case, on is the preposition. It tells us where the hat was.
- He unsuccessfully hid the hat behind his back.
- In this case, behind is the preposition. It tells us where the hat is.
In this post, we’re going to go over what prepositional phrases are, tips for understanding prepositional phrases, and how to use them effectively in a sentence.
Once we’ve reviewed the fundamentals, you’ll be able to test yourself with a post-assessment quiz, and practice with our high quality, standards-aligned questions here.
What We Review
What is a Prepositional Phrase?
A phrase is a group of words that work together conceptually as part of a sentence, but cannot stand on its own. It can have either a subject or a verb, but not both. It cannot stand on its own as a complete thought.
A prepositional phrase contains a preposition, its object, and any modifiers. It usually acts as an adverb or an adjective; however, it can sometimes act as a noun.
I edged closer to the wall.
- To is the preposition. To the wall is the prepositional phrase. This prepositional phrase is acting as an adverb, modifying closer.
They ‘d formed a committee of teachers from the district.
- Of and from are the prepositions. The prepositional phrase “of teachers” acts as an adjective, modifying committee. The prepositional phrase “from the district” acts as an adjective, modifying teachers.
In the middle of the bustling crowd, I saw him.
- In and of are the prepositions. The prepositional phrase “in the middle” acts as an adverb, modifying saw. “Of the bustling crowd” acts as an adjective, modifying crowd.
Pro tip: Think space and time! Prepositional phrases (minus some exceptions) will always give you more information about space and time.
The Ultimate List of Prepositions
Return to the Table of Contents
3 Tips for Understanding Prepositional Phrases
Here are some important tips to help deepen your understanding of prepositional phrases:
Tip #1: Remember that prepositional phrases need an object.
When considering prepositional phrases, it is important to remember that they need an object.
- I gazed below.
- In this case, below is an adverb modifying gazed.
- I gazed below the deck.
- In this case, below the deck is a prepositional phrase. Below is the preposition, and it modifies “gazed.” “Deck” is the object of the preposition. The phrase acts as an adverb would, but is considered a prepositional phrase because it includes an object.
Tip #2: Prepositional phrases add additional non-essential information.
There can be multiple prepositional phrases in a sentence or none at all. Prepositional phrases add additional-not essential-information.
The rover landed (1) on the planet’s surface immediately (2) after losing communication (3) with mission control. (As you can see, there are three prepositional phrases in this sentence.)
The rover landed. (There are none here, but this still counts as a complete sentence with a subject and verb.)

Tip #3: Master all the other parts of speech in order to then master prepositional phrases.
Honestly, learning about prepositions (and prepositional phrases) without learning about the other parts of speech will make it much more difficult.
Learning about all of the parts of speech and how they work together will help immensely. Practice with Albert’s Grammar course here.
Think about prepositional phrases as details that give writing clarity. While they’re not essential, they’re helpful for painting a more vivid picture with your words.
Return to the Table of Contents
Prepositional Phrases Exercises for Review
Identify the prepositional phrases in the sentences below.
1. I doodled in my notebook.
a. In my notebook is the prepositional phrase. It acts as an adverb, modifying “doodled.”
2. The boat navigated the choppy waters with purpose.
a. With purpose is the prepositional phrase. It acts as an adverb, modifying “navigated.”
3. They made raucous noise during the show.
a. During the show is the prepositional phrase. It acts as an adverb, modifying “made.”
4. The sight of the beach made me exhale deeply.
a. Of the beach is the prepositional phrase. It acts as an adjective, modifying “sight.”
5. After the party, I strolled home happily.
a. After the party is the prepositional phrase. It acts as an adverb, modifying “strolled.”
Return to the Table of Contents
Try for Yourself: Prepositional Phrases Quiz
1. True or false: Prepositional phrases only contain prepositions.
- Answer: False
- Correct Explanation: Correct! Prepositional phrases include prepositions, their objects, and any modifiers.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that is incorrect. Prepositional phrases include prepositions, their objects, and any modifiers.
2. True or false: Prepositional phrases are an essential part of a complete sentence.
- Answer: False
- Correct Explanation: Correct! You don’t need a prepositional phrase to write a complete sentence, but they do add more important detail.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that is incorrect. Prepositional phrases add important but nonessential information to a sentence.
3. How many prepositional phrases does this sentence contain?
She slid the king across the chessboard.
- Answer: One
- Correct Explanation: Correct! “Across the chessboard” is the only prepositional phrase. It tells us where she slid the king.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that is incorrect. “Across the chessboard” is the only prepositional phrase.
4. What is the preposition in this sentence?
The poodle sprung onto the couch.
- Answer: Onto
- Correct Explanation: Correct! “Onto” is the preposition. “Couch” is the object of the preposition.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s incorrect. “Couch” is part of the prepositional phrase, but it is not the preposition. It is the object of the preposition.
5. What is the prepositional phrase in this sentence?
After awhile, the tiny sapling grew tall.
- Answer: After awhile
- Correct Explanation: Correct! “After awhile” is the prepositional phrase. It acts as an adverb, modifying “grew.”
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s incorrect. “Grew” is a verb, and “tall” is an adjective, not a preposition.
Remember, Albert’s grammar course can help you gain confidence in identifying prepositional phrases and better understand how language works. Give it a try!
Return to the Table of Contents
Teacher’s Corner for Prepositional Phrases
The Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that students must “choose words and phrases to convey ideas precisely” from grades four through six. They then must “choose language that expresses ideas precisely and concisely, recognizing and eliminating wordiness and redundancy” through high school.
As prepositional phrases are used to add detail, they can be incorporated into a developmentally-appropriate curriculum at any age.
Grammar skills require consistent, low-stakes practice and quality feedback. Students benefit enormously from working at their own pace, as well. Albert’s grammar course is an invaluable resource that allows students the practice they need at the pace that’s best for them.
You can use our assessments to measure student progress, or create your own using our assignments feature.
Summary on Prepositional Phrases
A preposition expresses relationships between nouns. It can be used to indicate location, time, direction, and position.
A prepositional phrase contains a preposition, its object, and any modifiers.
In writing, prepositional phrases are details that paint a clearer picture in the reader’s mind. Although they aren’t essential as part of a complete sentence, they are an important part of well-crafted writing.
It is easier to learn about prepositional phrases as you are learning the other parts of speech. Visit Albert’s grammar course for in-depth explanations, practice quizzes, and assessments on nearly every grammar concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.









