Reflexive pronouns and intensive pronouns may look exactly the same, but they serve very different functions in sentences.
Think about the show Property Brothers. Jonathan and Drew Scott are identical twins with differing roles on their show. Jonathan takes the role of contractor while Drew takes the role of realtor.
Reflexive and intensive pronouns are similar. While they resemble one another, they play different roles in sentences.
For example:
The pronoun himself can be either a reflexive or an intensive pronoun, depending on how it is used. A reflexive pronoun reflects back on the subject of the sentence while an intensive pronoun adds emphasis or intensity to a noun.
- Reflexive: Drew decided to treat himself to a fancy dinner.
- Intensive: Jonathan built the shed in the backyard all by himself.

When you’re ready to review reflexive/intensive pronouns, test yourself with a quiz and practice with our high-quality, standards-aligned questions here.
What We Review
The Basics of Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns
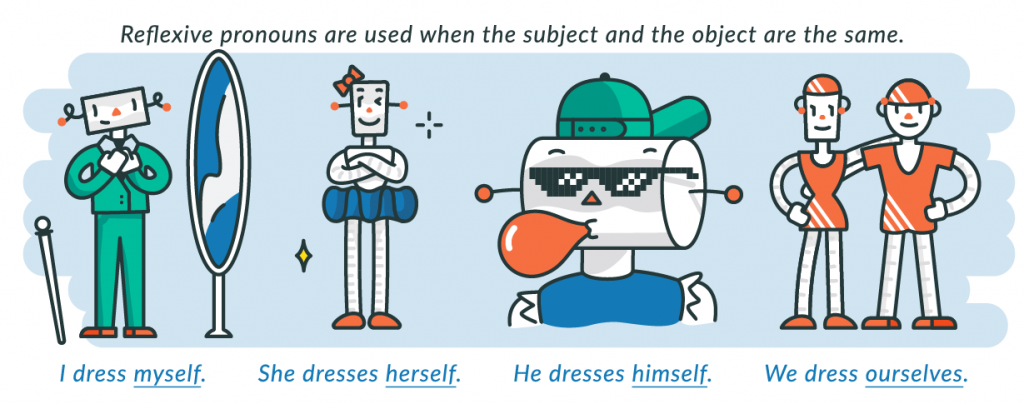
What is a Reflexive Pronoun?
A reflexive pronoun is a pronoun that “reflects” directly back onto the subject of the sentence. These pronouns always end in -self or -selves, such as himself or themselves, and they are essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence.
For example:
- The Robinsons were annoying neighbors; they kept inviting themselves over to our house!
What is an Intensive Pronoun?
An intensive pronoun is a pronoun that intensifies the subject. These pronouns also end in -self or -selves, such as herself or ourselves, but they are not essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence.
For example:
- The Robinsons themselves showed up uninvited to our house last night!
How are reflexive pronouns different from intensive pronouns?
Even though reflexive and intensive pronouns both compliment the subject in some way, the huge difference between reflexive and intensive pronouns is that when you remove a reflexive pronoun from a sentence, the sentence feels incomplete. If you were to remove an intensive pronoun from a sentence, the meaning of the sentence would not change.
Here is an example of a nonessential intensive pronoun:
- “She completed the marathon herself without the help of anyone”
vs.
- “She completed the marathon without the help of anyone”.
Do you see how the meaning of the sentence stays the same whether there is an intensive pronoun or not?

Now, here is an example of an essential reflexive pronoun:
- “He had to force himself to work out each morning in order to achieve his fitness goals”
vs.
- “He had to force to work out each morning in order to achieve his fitness goals”.
Do you see how the sentence without the reflexive pronoun does not make sense? The reader is left wondering who was forced to work out each morning.

3 Tips for Understanding Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns
Here are some important tips to help you understand and distinguish these two types of pronouns:

Tip #1. Reflexive Pronouns reflect back on the subject and are essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence
For example:
- She convinced herself to enroll in all AP® courses next school year.
In this sentence, herself is essential and reflects back on the subject to show that both the subject and object of the sentence refer to the same person.

Tip #2. Intensive Pronouns intensify or add emphasis to the subject of the sentence and are not essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence
For example:
- In Matilda, Bruce is forced to eat an entire chocolate cake himself.
In this sentence, himself is nonessential and is only used to emphasize the enormity of Bruce’s task of eating an entire cake, alone.

Tip #3. Both Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns always end in -self or -selves
For example:
A sentence would be incorrect if it read:
- I bought me a subscription to Disney+.
Whether the direct object reflects or intensifies the subject of the sentence, the pronoun must end in either -self or -selves depending on whether the noun is singular or plural.
Instead, the sentence should read:
- I bought myself a subscription to Disney+.

Applying the Basics: Reflexive and Intensive Pronoun Review & Practice
Now that you understand how reflexive and intensive pronouns function in sentences, review the anchor chart below and complete the review to fully understand how to use and recognize these two types of pronouns.
The Ultimate List of Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns
Refer to the graphic below to learn the nine reflexive and intensive pronouns:
Reflexive and Intensive Pronoun Exercises and Review
Now that you know how to recognize reflexive and intensive pronouns, test your ability to tell the difference between reflexive and intensive pronouns in sentences.
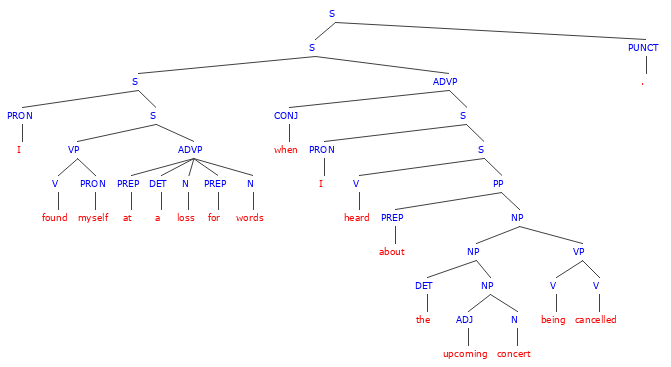
Select the Reflexive Pronoun in the sentences below. Remember, reflexive pronouns reflect directly back onto the subject of the sentence and are essential.
1. I found myself at a loss for words when I heard about the upcoming concert being cancelled.
- In this sentence, myself is a reflexive pronoun that shows the reader that both the subject and the object of the sentence refer to the same person.
2. He disappointed himself with his actions.
- In this sentence, himself is a reflexive pronoun to show that the subject and the object refer to the same person.
3. She lost herself in the overwhelming beauty of the enchanted forest.
- In this sentence, herself is a reflexive pronoun that reflects back to the subject of the sentence, showing that the object and subject of the sentence are the same person.

Select the Intensive Pronoun in the sentences below. Remember, intensive pronouns intensify or add emphasis to the subject of the sentence and are not essential.
4. If you have younger siblings, you are probably used to hearing them say, “I can do it myself!”
- In this sentence, myself is an intensive pronoun that emphasizes the younger sibling’s ability to do something without anyone else’s help.
5. She scored an audition to be in the musical herself.
- In this sentence, herself only adds emphasis as an intensive pronoun and is not essential to understanding the sentence.

Pro tip: When deciding whether a pronoun is reflexive or intensive, try removing it from the sentence in your head. If the sentence is confusing without the pronoun, then it is reflexive, but if the sentence can stand on its own without the pronoun, then it is intensive.
For additional practice, check out the Reflexive Pronouns content on Albert.
Try for Yourself: Reflexive and Intensive Pronoun Quiz

Feeling confident in your understanding of Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns?
Take this short six-question quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Can a reflexive pronoun be removed from a sentence and the sentence still make sense?
- Answer: No
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! A reflexive pronoun is essential to understanding the sentence and therefore cannot be removed.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, a reflexive pronoun is essential to understanding the sentence and therefore cannot be removed, while an intensive pronoun is not essential to the sentence.
2. Do intensive pronouns and the subject of the sentence ultimately refer to the same noun?
- Answer: Yes
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Whether you use a reflexive or an intensive pronoun, they are both used to compliment the subject of the sentence in some way and refer to the exact same noun.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, whether you use a reflexive or an intensive pronoun, they are both used to compliment the subject of the sentence in some way and refer to the exact same noun.
3. In this sentence, is the word, “itself” a reflexive or intensive pronoun?
The cat licked itself clean with its sandpaper-like tongue.
- Answer: Reflexive
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The pronoun itself refers back to the cat, the subject of the sentence to show who the cat was cleaning.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, reflexive pronouns reflect back to the subject of the sentence, showing that the object and subject of the sentence are the same person.
4. In this sentence, is the word, “herself” a reflexive or intensive pronoun?
She created a business plan and opened a thriving cafe herself.
- Answer: Intensive
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The pronoun herself is an intensive pronoun because it emphasizes the subject of the sentence without being essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, an intensive pronoun intensifies or adds emphasis to the subject of the sentence and is not essential.
5. In this sentence, is the word, “ourselves” a reflexive or intensive pronoun?
After our home was destroyed by a tornado, we rebuilt a home ourselves.
- Answer: Intensive
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The pronoun ourselves is an intensive pronoun because it emphasizes the subject of the sentence without being essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, an intensive pronoun intensifies or adds emphasis to the subject of the sentence and is not essential.
6. In this sentence, is the word, “themselves” a reflexive or intensive pronoun?
They checked themselves in at the hotel since it was past midnight.
- Answer: Reflexive
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Themselves is reflexive because it reflects back to the subject of the sentence and is essential to understanding the meaning of the sentence.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, reflexive pronouns reflect back to the subject of the sentence, showing that the object and subject of the sentence are the same person.
For additional practice with Reflexive Pronouns, check out our practice on Albert: Reflexive Pronouns.
Teacher’s Corner for Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns
As teachers, we know that oftentimes the way that our students speak in casual conversation is very different from how their formal writing should appear. The Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart is a helpful resource for teachers in helping tackle some of these grammatical misconceptions as students grow and develop.
For specific standards on the different types of pronouns including reflexive and intensive pronouns, check out the Common Core State Standards website.
Albert has several tools available for teachers including both a topic-specific Reflexive Noun Practice and full-scale Grammar assessments which can be assigned by teachers to focus on a specific group of skills.
Summary for Reflexive and Intensive Pronouns
Be sure to check out our grammar course for more reflexive and intensive pronoun practice.
You can also access over 3,400 high-quality questions that address nearly every grammatical concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.









