Nouns and verbs can both express number, but only verbs can express tense, or when the action of the sentence is performed or a state of being is experienced.
Keeping tense clear and consistent throughout one’s writing is essential, but it is often overlooked by writers wanting to rush through their work. Getting in the habit of establishing your verb tense early on and sticking with it helps in two ways: first, your writing will flow more smoothly; second, you will avoid a large chunk of editing later on.
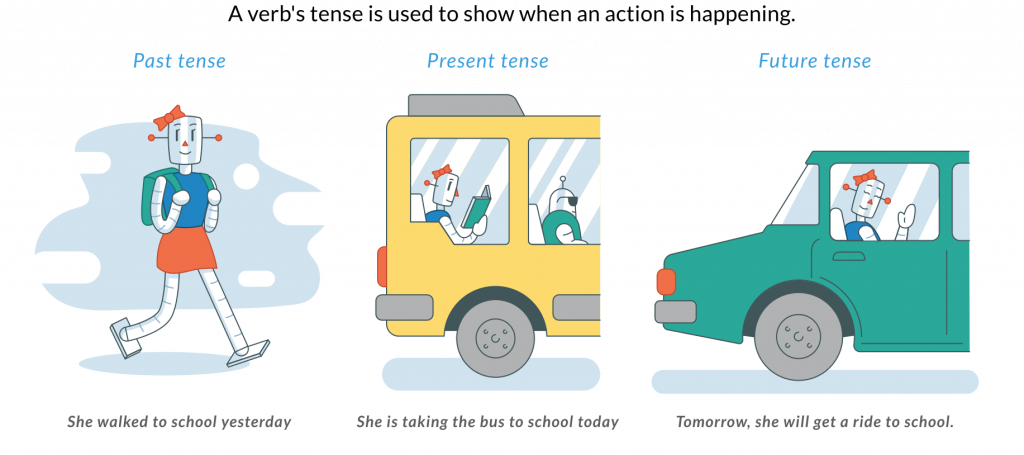
While there are several different types of verb tenses, the foundational tenses are past, present, and future. These are called simple verb tenses.
There are also perfect verb tenses, progressive verb tenses, and there are even some irregular verbs that do not follow the rules when changing tense. While this blog post focuses on simple verb tenses, these other verb tenses can be explored in other blog posts on Albert.
When you’re ready, test yourself with a quiz and practice with our high-quality, standards-aligned questions here.
What We Review
The Basics of Simple Verb Tenses
What is Simple Verb Tense?
Simple verb tense can be divided into three categories: past, present, and future.
- Present Tense: He writes a letter today.
- Past Tense: I wrote a letter yesterday.
- Future Tense: I will write a letter tomorrow.

While some verb tenses, such as present tense and past tense, can be expressed by simply changing the form of the verb itself, other verbs need the help of an auxiliary verb to show tense, especially future tense.
In the examples above, the present tense verb, writes, looked only slightly different in past tense, wrote. However, this same verb needs the auxiliary verb, “will” joined with the present tense form of the verb, write to create future tense.
How is Simple Past Tense Used in Academic Writing?
Student writers use simple past tense verbs to describe something that happened prior to the current action in a narrative, an author’s ideas in a literary essay, or historical events in a research paper.
For example:
- Narrative: The charred wallpaper peeling mournfully from the walls indicated that a fire had broken out sometime overnight.
In this example, the narrator makes an assumption about an event that occurred earlier in the story.
- Literary Essay: Inspired by her own childhood, Harper Lee crafted Jean Louise “Scout” Finch in close resemblance to herself.
In this example, the student writer analyzes Harper Lee’s novel, To Kill a Mockingbird, focusing on how this novel originated during the 1960’s.
- Research Paper: When Disney World first opened in 1971, tickets were only $3.50.
In this example, the student writer uses simple past tense to share historical information.

How is Simple Present Tense Used in Academic Writing?
Student writers use present tense in narratives to describe what is happening in the current moment, in scientific papers to state facts, or in literary analyses to incorporate the writer’s own ideas.
For example:
- Narratives: He steps through the open portal, and he finds himself in another dimension.
- Scientific Writing: Many creatures in the natural world, such as frogs, still experience the stages of evolution.
- Literary Analysis: I am proud of Harper Lee for using her skilled voice as a writer to speak out against racial injustice.

How is Simple Future Tense Used in Academic Writing?
Simple future verb tense is used less often in academic writing than simple present or simple past tense, but that does not mean it is any less important.
In narrative writing, students can take the role of an omniscient or all-knowing narrator that can share the future for his or her characters.
For example:
- Narrative: He has no idea that his decision will lead to his tragic downfall.
How is Simple Verb Tense Different from Perfect Verb Tense?
While simple verb tense can express an action that did happen, is happening, or will happen, the perfect verb tense indicates an action that has already been completed or “perfected”. The perfect verb tense always appears with the auxiliary verb have or had. You can learn more about perfect verb tenses in this blog post.
For example:
- Simple present: I eat my lunch.
- Present perfect: I have eaten my lunch.
- Simple past: I walked to school yesterday.
- Past perfect: I had walked to school yesterday.
- Simple future: I will finish my homework tomorrow.
- Future perfect: I will have finished my homework by tomorrow.
How is Simple Verb Tense Different from Progressive Verb Tense?
While simple verb tense expresses an action that did happen, is happening, or will happen and perfect verb tense expresses an action that has already been completed, progressive verb tense expresses an ongoing action. Progressive verb tense always uses a form of the “to-be” verb and an -ing verb.
- Simple present: I ate my lunch.
- Present progressive: I am eating my lunch.
- Simple past: I walked to school yesterday.
- Past progressive: I was walking to school yesterday.
- Simple future: I will finish my homework tomorrow.
- Future progressive: I will be finishing my homework by tomorrow.
Return to the Table of Contents
3 Tips for Understanding Simple Verb Tenses
Here are some important tips to help you understand simple verb tense:

Tip #1. Facts and current actions are always written in simple present tense
For example:
- Many plants need sunlight and water to survive.
Tip #2. Historical events, events in the past, and author’s decisions are all written in simple past tense
For example:
- Inspired by ancient Greek games, the international Olympics started in 1896.
Tip #3. Verb tense must stay consistent in your writing to avoid confusion

For example:
- Incorrect: The hockey game last night was brutal; no one scores until the third period.
Because the initial verb in this sentence is in past tense, the second verb also must be in past tense. See the corrected sentence below:
- Correct: The hockey game last night was brutal; no one scored until the third period.
Return to the Table of Contents
Applying the Basics: Simple Verb Tenses Review & Practice
Now that you understand how simple verb tense functions in sentences, review the anchor chart below and complete the review to fully understand how to use and recognize simple verb tense as well as how to differentiate it from other verb tenses.
The Ultimate List of Verb Tenses
Refer to the graphic below to learn the different types of Verb Tenses:
This list, obviously, does not include all possible verbs and their tenses; however, it is meant to be used as a guide while identifying different types of verb tenses.
Simple Verb Tense Exercises and Review
Now that you understand simple verb tense, test your ability to recognize which verb tense in needed in the sentences below:
Select the correct verb tense in the sentences below. Remember, past verb tense describes events that happened in the past, present verb tense describes events that are happening currently, and future verb tense describes events that are yet to happen.
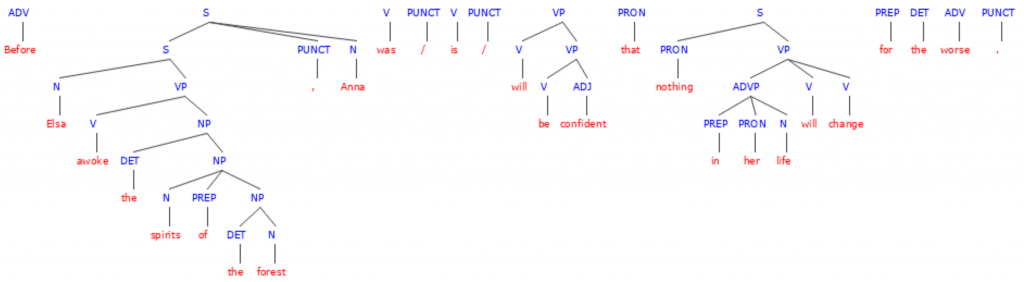
1. Before Elsa awoke the spirits of the forest, Anna was/is/will be confident that nothing in her life will change for the worse.
In this sentence, was is the correct verb tense to use. Since the context clues in the sentence reference something that happened earlier in the movie, a simple past tense verb is needed.
2. Throughout the movie, it is/was/will be clear that Elsa regretted ever trusting Prince Hans of the Southern Isles.
In this sentence, was is the correct verb to use. We know this because another simple past tense verb is used later in the sentence: regretted. In order to be consistent in our use of verb tense, both verbs must be in past tense.
3. Once she finds out what really happened between Arendelle and the Northuldra tribe, Elsa is/was/will be determined to make things right.
In this sentence, “is” is the correct verb to use because it is in simple present tense, just like the other verb in the sentence, finds.
4. Olaf no longer needs his own snow flurry to stay frozen because last month, Elsa gives/gave/will give him permafrost.
In this sentence, gave, or the past tense form of the verb, is needed because the context clue, last month, implies that Elsa giving Olaf his permafrost happened in the past.
5. Grand Pabbie warns Elsa that bad things are happening/have happened/will happen if Elsa does not conquer the spirits of the forest.
In this sentence, will happen, or the future tense verb, is needed because the sentence sets up a contingent relationship. Because Grand Pabbie knows all, he can predict what will happen if Elsa is unsuccessful on her quest.
Pro tip: Simple verb tense can be narrowed down into three simple categories that show when an action occurred or when a state of being was experienced in a sentence. These three categories, past, present, and future, perform best when verbs of the same tense are used consistently within one piece of writing.
For additional practice, check out Simple Verb Tense content on Albert.
Return to the Table of Contents
Try for Yourself: Simple Verb Tenses Quiz

Feeling confident in your understanding of Simple Verb Tense?
Take this short six-question quiz to see what you’ve learned:
1. Which verb tense shows that the action in the sentence is ongoing: simple, perfect, or progressive?
- Answer: Progressive
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Progressive verb tense shows action that is ongoing while simple verb tense can show action that already happened, is happening, or will happen.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, progressive verb tense shows action that is ongoing while simple verb tense can show action that already happened, is happening, or will happen.
2. True or False: simple future verb tense can be expressed without the help of auxiliary verbs.
- Answer: False
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Simple future verb tense, unlike simple present or simple past tense, must have an auxiliary verb attached to it in order to express future tense.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, simple future verb tense, unlike simple present or simple past tense, must have an auxiliary verb attached to it in order to express future tense.
3. In this sentence, is the present tense verb, “have finished” simple, perfect, or progressive tense?
I have finished sewing a quilt for my baby nephew.
- Answer: Perfect Verb Tense
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The verb have finished expresses an action that has already been completed, so it must be a perfect verb tense.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, perfect verb tenses express actions that have already been completed, so have finished is perfect, not simple or progressive.
4. In this sentence, is the past tense verb, hiked, simple, perfect, or progressive tense?
We hiked a large section of the Smoky Mountain National Park yesterday.
- Answer: Simple Verb Tense
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! The past tense verb, hiked, expresses an action that was done on the previous day, or in the past. Since the action is not explicitly ongoing or completed (they may hike more today), the tense is simple past.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, simple past tense expresses an action that happened in the past, not one that is ongoing or one that has been completed.
5. In this sentence, is the future tense verb, will be attending, simple, perfect, or progressive tense?
They will be attending the awards ceremony this evening.
- Answer: Progressive verb tense
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! In this sentence, the phrase will be attending implies an ongoing activity that will occur in the future; therefore, a future progressive verb is required.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, future progressive verb tense implies an ongoing activity that will occur in the future, such as, will be attending.
6. In this sentence, is a simple past or simple present tense verb needed?
While we were trick-or-treating last night, I bump/bumped into someone that looked like Frankenstein’s monster.
- Answer: bumped: simple past tense
- Correct Explanation: That’s right! Since the tense of the first verb in the sentence is past (were), the tense of the second verb also needs to be past, which is bumped.
- Incorrect Explanation: Sorry, that’s not right! Remember, in order to be consistent in your writing, if another verb in the sentence is past tense, then any subsequent verbs must also be in past tense.
For additional practice with Simple Verb Tense, check out our practice on Albert: Simple Verb Tense.
Return to the Table of Contents
Teacher’s Corner for Simple Verb Tenses
How many times have you read a student’s paper only to find that the verb tense changes nearly every sentence? Oftentimes students do not realize the importance of consistency when it comes to verb tense. Even though students may understand the fundamentals of subject and verb usage in a sentence, the Common Core English Language Progressive Skills Chart shows that there are always ways to build on students’ knowledge and create even stronger writers.
Albert provides several different verb tense practice activities, including Simple Verb Tense Practice. Albert has also created full-fledged assessments and quizzes on a range of grammatical topics.
Summary for Simple Verb Tenses
There are many verb tenses out there to choose from, but the most important thing is choosing the right tense for the type of writing you are doing and then sticking with it!
Be sure to check out our grammar course for more Simple Verb Tense practice.
You can also access over 3,400 high-quality questions that address nearly every grammatical concept.
Need help preparing for your Grammar exam?
Albert has hundreds of grammar practice questions with detailed explanations to help you master concepts.