In this post, we’ll cover the basics of atomic structure. We will review the components of an atom, the atomic number, atomic mass, and the difference between elements and compounds. By the end of this post, you’ll have a solid understanding of the atom and its role in chemistry.
What We Review
What is the Structure of an Atom?
Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter. The atom consists of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each component has a unique role in the structure of an atom. The way these components interact can also determine an atom’s properties.
Protons
Protons are positively charged particles located in the nucleus of an atom. Each proton has a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (\text{amu}), or 1.67 \times 10^{-27}\text{ kilograms}. The atomic number refers to the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It also helps to determine the identity of the element. For example, all carbon atoms have 6 protons in their nucleus, while all oxygen atoms have 8 protons.
Neutrons
Neutrons are neutral particles that are also found in the nucleus of an atom. Like protons, they have a mass of approximately ]latex]1 \text{ amu}[/latex]. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary. Isotopes refer to atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. As you’ll soon see, isotopes of an element have the same atomic number but different atomic masses.
Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom in shells. At 9.11\times 10^{-31}\text{ kg}, they have a much smaller mass than protons and neutrons. They are also responsible for the chemical properties of an element. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, which makes the atom electrically neutral.
View the video below for an overall review of the atom. In the next section, we’ll explore the atomic number and mass and how they relate to the structure of an atom.
Atomic Number
What is the Atomic Number?
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons found in its nucleus. This number is unique to each element. We represent the atomic number with the symbol Z. For example, the atomic number of carbon is 6 because a carbon atom has 6 protons in its nucleus.
The Atomic Number on the Periodic Table
The periodic table organizes elements by their atomic number. Elements in the periodic table increase in atomic number as you go across the rows and columns. Each column is a group and each row is a period. Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and similar chemical properties. For example, all elements in group 1 of the periodic table have one valence electron and are highly reactive metals.
To find the atomic number of an element, simply look at its place in the periodic table. The atomic number is the value above the element’s symbol in the table. For example, the atomic number of lithium (Li) is 3, as it is the third element in the periodic table.
Let’s take the example of nitrogen, which has an atomic number of 7. This means that a nitrogen atom has 7 protons in its nucleus as well as 7.
Atomic Mass
What is the Atomic Mass?
The atomic mass of an atom is the mass of the atom’s nucleus. This is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. The atomic mass is usually expressed in atomic mass units (\text{amu}). For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.01\text{ amu}. You can calculate this as the sum of its 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
What is the Difference Between Atomic Mass and Atomic Number?
The atomic number and atomic mass are two different properties of an atom. The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Meanwhile, the atomic mass represents the mass of the nucleus. Recall that this is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons.
While the atomic number is a whole number, the atomic mass of an element may not be a whole number. This is because of the existence of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, while carbon-14 has 6 protons and 8 neutrons. The atomic mass of carbon is the weighted average of the atomic masses of its isotopes. Therefore the atomic mass of carbon is approximately 12.01\text{ amu}.
To calculate the atomic mass, you need to know the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For example, nitrogen has an atomic number of 7 and an atomic mass of approximately 14.01\text{ amu}. This means that a nitrogen atom has 7 protons and 7 neutrons in its nucleus.
Atoms on the Periodic Table
The periodic table provides a summary of all of this information. The atomic number, located at the top of the element’s box, indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. The symbol represents the shorthand for the element’s name. Lastly, the atomic mass or atomic weight, located at the bottom of the element’s box, indicates the average mass of an atom of that element.
Consider the example below for Boron. The B is the symbol for Boron. The value 5 in the top corner is the atomic number and the value 10.811 is the average atomic mass.
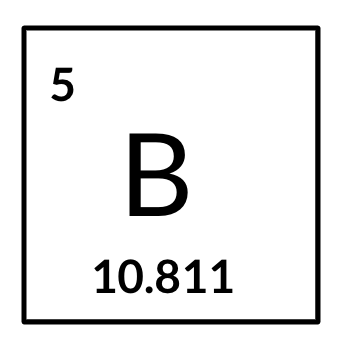
Practice reviewing more elements on the periodic table with these examples.
Elements and Compounds
What is an Element?
Chemical means cannot break down an element, which is a pure substance. Atoms, which have the same number of protons in their nucleus, make up each element. This gives them the unique atomic number we just discussed. Scientists organize elements by their atomic number on the periodic table.
An example of an element is gold (Au). Many people value gold for its lustrous yellow color. In its pure form, gold atoms all have 79 protons in their nucleus, giving it an atomic number of 79.
What are Compounds?
A compound is a substance that is made up of two or more different elements that are chemically combined in a fixed ratio. The atoms in a compound are held together by chemical bonds. With the right amount of energy, someone or something can break the bonds holding the compounds together.
An example of a compound is water (H_2O). Water is a colorless, odorless liquid that is essential to life on Earth. Water molecules consist of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
What is the Difference Between an Element and a Compound?
The main difference between an element and a compound is that elements are made up of only one type of atom and compounds are made up of two or more different atoms.
Another key difference is that elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. On the other hand, compounds can be broken down into their individual elements. Elements have unique physical and chemical properties. The properties of a compound can be different from the properties of its constituent elements.
An example of the difference between an element and a compound is sodium (Na) and sodium chloride (NaCl). Sodium is a soft, silvery metal that is highly reactive. Meanwhile, sodium chloride is a white crystalline solid that is commonly known as table salt. Sodium consists of only one type of atom, while sodium chloride is a compound that is made up of both sodium and chlorine atoms. For NaCl, they are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio of 1:1.
Conclusion
Understanding the structure of an atom and its properties is crucial to understanding the behavior of matter. The atomic number and atomic mass are ways to define and describe pure elements. Now that we understand the structure of the atom, we can apply this knowledge to the elements and compounds all around us.